Options Trading
It is important to understand the basics of trading options before entering the market. Speculating on this type of derivative is popular with traders in the UK, offering access to stocks, indices and commodities, among other assets. In this guide to trading options, we look at strategies for beginners, how to find and capitalise on live opportunities, plus tips for getting started. We also list the best brokers and platforms for trading options in 2025.
Brokers with Options Trading
-
Founded in 1974, IG is part of IG Group Holdings Plc, a publicly traded (LSE: IGG) brokerage. The brand offers spread betting, CFD and forex trading across an almost unrivalled selection of 17,000+ markets, with a range of user-friendly platforms and investing apps. For 50 years, IG has maintained its position as an industry leader, excelling in all key areas for traders.
-
Founded in 1999, FOREX.com is now part of StoneX, a financial services organization serving over one million customers worldwide. Regulated in the US, UK, EU, Australia and beyond, the broker offers thousands of markets, not just forex, and provides excellent pricing on cutting-edge platforms.
-
Established in 2001, easyMarkets has made for a name for itself as a trusted, fixed spread broker. Improvements to its tools over the years, from adding the MetaTrader suite and TradingView to enhancing its exclusive risk management tools like dealCancellation, mark it out from the competition.
-
Established in 2008 and headquartered in Israel, Plus500 is a prominent brokerage that boasts over 25 million registered traders in over 50 countries. Specializing in CFD trading, the company offers an intuitive, proprietary platform and mobile app. It maintains competitive spreads and does not charge commissions or deposit or withdrawal fees. Plus500 also continues to shine as one of the most trusted brokers with licenses from reputable regulators, including the FCA, ASIC and CySEC.
-
Established in 1983 and now a part of the Nasdaq-listed StoneX Group, City Index is a renowned and award-winning broker specializing in forex, CFDs, and spread betting. Offering over 13,500 instruments, an evolving Web Trader platform, top-tier educational resources, and 24/5 customer support, City Index delivers a comprehensive trading experience.
-
Spreadex is an FCA-regulated broker that offers spread betting opportunities on an impressive 10,000+ CFD instruments including 60 forex pairs. Traders can also take short-term positions on sporting events. The brand has been around for over 20 years and has won multiple awards.
-
NinjaTrader is a US-headquartered and regulated brokerage that specializes in futures trading. There are three pricing plans to suit different needs and budgets, as well as ultra-low margins on popular contracts. The brand's award-winning charting software and trading platform also offers a high-degree of customization and superb technical analysis features.
-
Interactive Brokers (IBKR) is a premier brokerage, providing access to 150 markets in 33 countries, along with a suite of comprehensive investment services. With over 40 years of experience, this Nasdaq-listed firm adheres to stringent regulations by the SEC, FCA, CIRO, and SFC, amongst others, and is one of the most trusted brokers for trading around the globe.
-
Webull is a multi-regulated trading app that offers stocks, options, forex, cryptos, ETFs, fractional shares and more. The firm is authorized by the SEC, FINRA and FCA and continues to uphold a strong trust rating. Low fees, no minimum investment and generous welcome bonuses have made the discount broker popular with online investors.
-
Trade.com is a trustworthy online broker with a global presence. The broker offers 2,100+ CFDs in major markets, as well as futures, options and more. The broker offers best-in-class platforms and superior analysis tools for experienced traders. The broker is also regulated by top-tier authorities including the FCA and CySEC.
-
RockGlobal is a New Zealand based and regulated CFD broker. They offer competitive spreads from 0.1 pips and a large range of trading assets, trading platforms and educational services, with up to 1:500 leverage. Operating in a Tier 1 regulated environment, RockGlobal offers peace of mind and excellent customer support.
-
Firstrade is a US-headquartered discount broker-dealer with authorization from the SEC. The company is also a member of FINRA/SIPC. With welcome bonuses, powerful tools and apps, plus commission-free trading, Firstrade Securities is a popular and top-tier online brokerage. It is also quick and easy to open a new account.
-
Established in 1996, Swissquote is a Switzerland-based bank and broker that offers online trading on an industry beating three million products, from forex and CFDs to futures, options and bonds. Highly trusted, it has built a strong reputation through innovative trading solutions, from becoming the first bank to offer crypto trading in 2017 to more recently launching fractional shares and its Invest Easy service.
-
Infinox is a UK-based and FCA-regulated broker that offers diverse trading products thanks to its STP and ECN account types and support for MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5 and a proprietary platform. Clients can also benefit from a free VPS that can support automated strategies and a social trading platform, catering to both beginner and seasoned traders.
-
Saxo Markets is a multi-award-winning trading brokerage, investment firm and regulated bank. With a huge 72,000+ trading instruments, plus investment products and managed portfolios, clients have no shortage of opportunities. The trusted brand also offers transparent pricing and top-tier regulatory protection from 10+ agencies including FINMA, FCA & ASIC.
-
Zacks Trade is a FINRA-regulated US broker offering trading on stocks, ETFs, cryptocurrencies, bonds and more through a proprietary terminal. The broker is geared toward active traders and offers very affordable fees on most assets as well as an app and a vast amount of market data.
-
Just2Trade is a reliable multi-regulated broker registered with FINRA, NFA and CySEC. The company has 155,000 clients from 130 countries and stands out for its huge suite of instruments and additional features, including a social network, robo advisors and a funded trader programme.
-
BinaryCent is an unregulated binary options broker that offers 24/7 trading on forex, cryptos and stocks with payouts up to 95%. Despite its lack of regulation, this broker takes client security seriously and stores client funds in European banks. The broker also offers CFDs with very high leverage up to 1:500.
-
FXPrimus is an award-winning CySEC-regulated brokerage offering CFD trading on 200+ instruments via the MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5 and cTrader platforms. The choice between a competitive commission-free account and two affordable raw spread options make this an accessible broker for anyone seeking forex, stocks, indices and commodities with high leverage.
Trading Options Explained
An options trading contract is a legal and binding agreement between a trader and a broker that permits the trader to buy or sell an asset at a pre-agreed time and price. For example, trader X wants the option to buy 10 shares in BP at £450 per share at the end of the month.
The buyer has the right to exercise the options contract but is not compelled to do so (a key difference versus futures). The seller is obligated to meet the transaction terms of the contract if the option is exercised before or on the expiration day.
Importantly, the buyer will pay a premium for the right to exercise the options contract. This cost will depend on the price of the asset and its intrinsic and extrinsic value – the difference between the contract’s strike price and the current price of the asset.
An investor trading options will use calls when buying an asset and puts when selling an asset. Standard options contracts are also known as ‘vanilla options’.
Options trading ultimately allows investors to take positions on:
- A rise or fall in the current value of an asset
- The extent to which an asset’s price will rise or fall
- When these price fluctuations will take place
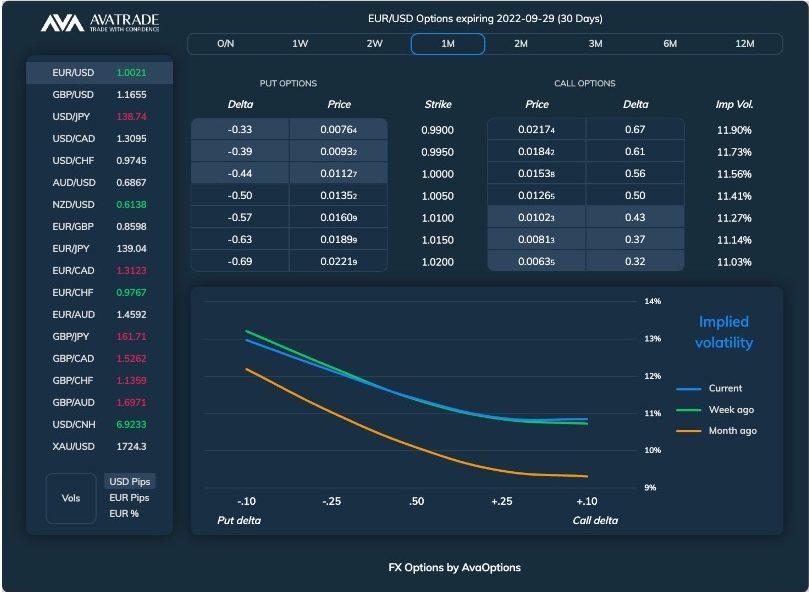
Trading Options At AvaTrade
How Does Trading Options Work?
Options contracts are derivatives which means they derive their value from an underlying asset. Underlying assets can span various markets, from FTSE-listed stocks and precious metals like gold to forex pairs with the GBP.
Both retail and institutional investors trade options with leverage. This means for a small capital outlay, they can take much larger positions than their cash would otherwise allow. This can significantly increase potential returns, making it a popular way to speculate on equities, for example, as opposed to directly buying and selling stocks.
Regardless of whether you are swing trading or day trading options, investors will often find the same rules and components in the products provided by online brokers. Each option requires details of the following to constitute a contract between the broker and trader:
- The underlying security
- The number of units/shares
- Type of option (put or call)
- Exercise/strike price (the price at which an option can be exercised)
- Expiration time and date (the time in which the trader can exercise the option)
Note, when you buy options, your risk exposure is normally capped to the premium you paid to take the position. However, when you sell options, your risk can be unlimited.
Example
To understand how an options trade works, let’s look at a standard stock purchase versus a leveraged options contract…
A trader has £1,000 to invest. Rolls Royce (RYCEY) stock is currently trading at £50 per share and therefore the trader can buy 20 shares. If the share price increases by 10% then each share increases to £55, taking the total portfolio value to £1,100. Excluding costs/commissions associated with the trade, the total gain from the trade is £100 (£1,100 – £1000).
Now let’s look at the potential returns if the trader buys Rolls Royce stock call options with a strike price of £50 that expires in two weeks. The shares cost £2 per share or £200 per contract (each contract holds 100 shares). With £1,000, the trader can buy five contracts or 500 shares. If the stock price increases 10% to £55 by the expiry, each contract will be worth £5 (£55 from a strike price of £50). Therefore, the total trade will be worth £2,500 on 500 shares, making a profit of £1,500.
In both examples, the amount of capital being risked is the same – £1,000. However, the key difference is that the potential profit is higher with the call options because of the leverage available.
Pros & Cons Of Trading Options
Pros
Benefits of trading options include:
- Greater Margins – Investors can make larger returns with the same capital via a margin account
- Cost Effective – The premiums for puts and calls are often cheaper than purchasing the underlying asset, making them popular with beginners
- Broad Market Access – Options contracts are available on a variety of markets, including stocks, indices, forex and commodity. This also means options contracts can be used for hedging
- Reduced Risk – Your risk exposure is often lower than directly trading the underlying asset. This is because the trader only stands to lose the premium paid for the option whereas the value of the asset bought outright could decrease significantly
Cons
There are also downsides to trading options:
- Complex – For new traders, options contracts are not the most straightforward instrument to understand. Fortunately, the best brokers offer a selection of beginner-friendly training content and free demo accounts
- Requires Active Trading – Options contracts, by definition, give traders the right to exercise the trade and therefore investors will need to keep a regular eye on their positions
- Fast Paced – Many retail trading platforms offer options contracts with short timeframes. The likelihood of an options contract spanning several months is unlikely, which may deter some retail traders
- Prices – Some brokers charge high commissions for short-term options contracts, for example weekly, versus the fees for buying stocks directly
- Taxes – UK traders may have to pay capital gains on profits
How To Start Trading Options
Comparing Brokers
Options trading is available at many top-rated brokerages. However, there are several elements to consider before opening an account:
Terms
Brokers need to remain profitable and therefore can hedge the risk of entering the contract with a trader by writing terms which will be favourable to them. This could be in the form of a high premium to enter the contract or an undesirable expiration time and date.
Trading Platform
The best platform for trading options is the one that works for you. For beginners, the platform you choose should make the basics easy to understand and enjoyable. The key things to consider are live charting functionality, technical analysis and the number of indicators available, automated and algorithmic trading opportunities, trend analysis, volume and volatility charts and historical data archives.
Some investors may also wish to trade options on a platform independent from their broker, such as TradingView.
Demo Account
Brokers who offer investors the opportunity to practice trading options under live conditions provide a significant advantage. A demo account will allow investors to enter paper trades in a simulator environment and test how strategies would have played out without risking their own capital.
The top brokerages then make it easy to switch to a real-money account when traders feel ready.
Apps For Trading Options
Nowadays it has become second nature to have access to our online life via our mobile devices. Financial trading is no different, so the top brokers provide a good quality mobile application, including Fidelity.
Investors should be able to speculate on different stocks, options and other financial instruments while on the go. This is particularly important with options contracts as a trader may be debating whether to exercise the option or not based on current market conditions.

Deposit & Withdrawal Methods
Payment methods are also a key factor when choosing an online broker. Most leading sites will provide their customers with many different ways to fund their accounts. This could be via debit/credit cards, wire transfers, e-wallets or even deposits via cryptocurrency.
Traders should be able to find payment method information on their broker’s website before they are asked to create an account.
Fees
When deciding on a broker to start trading options through, it’s important to assess the fee structure. Most brokers will be transparent with the costs associated with trading options, meaning they should provide information regarding charges and fees before users are required to sign up. As a result, traders will be able to assess the impact on earnings and the level of margin they should expect to receive.
Trading Hours
Options contracts will normally be bound by the trading hours of the underlying asset to which they are pegged. For example, a BT stock options contract will be tradable during the London Stock Exchange’s opening hours of 8:00 AM to 4:30 PM GMT.
Note, options trading is not usually available after hours unless the underlying asset is cryptocurrency.
Security & Regulation
When risking personal funds, it’s important to feel that your capital is relatively safe. Most leading options brokers will be governed by a reputable regulatory body such as the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA).
Beginners should take extra care when registering with a broker who is not FCA regulated as there will be fewer safeguards, for example, no limits on leveraged trading products.
Other key security procedures to look out for are encryption of sensitive data, zero balance protection and policies to protect the trader’s money if the broker goes into liquidation.
Other Features
It’s also worth looking at what additional features the brokerage has to offer. Some options brokers invest heavily to enhance the trading experience for their users.
Popular additional features include margin calculators, related news stories and market bulletins, and an education centre where the broker provides tips and tutorials on how to make money from trading options.
Research & Strategy
Since trading options is popular amongst investors of all levels, including beginners, there is a range of information available online that can help daily traders gain a better understanding of the assets they’re speculating on. Users can enrol in an online trading course with an independent provider or directly at some brokers.
Traders wanting a more traditional learning path may want to purchase print-based books on the internet or in-store. Popular books include Trading Options For Dummies, which has been touted as the best book on trading options for beginners. The publication looks at the different types of options and whether you can go negative.
UK traders wishing to review tips and educational resources for free can also make use of YouTube and Reddit. Here, experienced investors and market experts provide their opinions on key topics such as how to practice investing and how to be profitable when trading options.
When choosing a strategy, consider the underlying asset’s performance, your risk appetite and how active you plan to be. For example, day or intraday trading options contracts are quite demanding. Fortunately, most strategies can be supported by software or mobile alerts to keep you aware of market updates.
All strategies should also be supported with risk management techniques like stop-loss orders which can help ensure you don’t risk more than you can afford to lose.
Note, options trading is popular amongst beginners as well as professional investors who consider market trading as their full-time jobs. As a result, there is a catalogue of market tips, advice and information on options strategies available online.
Bottom Line On Trading Options
Trading options can be low-risk and high reward. Although a complicated concept to grasp for beginners, investors can make steady returns if used correctly. Make sure to practice options trading using a demo account before risking real money. Also implement risk management tools like stop-loss orders.
Use our list of the top options trading brokers and platforms in 2025 to get started.
FAQ
What Is Options Trading?
Options traders speculate on the future price of an underlying asset. The trader has the right but is not obliged to buy or sell the security. The underlying asset could be stocks, commodities, indices, cryptocurrencies, and other popular markets – the list of supported assets varies between brokers. Importantly, clients pay a premium for the flexibility to decide whether to exercise the trade.
Is Trading Options Profitable?
Options trading can be profitable with an effective strategy and a sensible approach to risk management. Reliable market insights, competitive puts and calls, plus a tested investing system will be needed to make money in the long run.
Is Trading Options Halal?
Trading options is prohibited under Sharia Law according to some Islamic scholars. This is because of the speculation involved and the opportunities to take positions in haram industries, such as alcohol and tobacco. With that said, some market commentators believe options trading can be halal. Consult a local religious leader for guidance. Alternatively, see our guide to halal trading for more information.
Does Trading Options Count As Day Trading?
Options products can be used to day trade. Day trading is essentially the practice of opening and closing positions in the same trading session. Binary options are also popular with short-term investors, especially beginners.
Can You Make Money Trading Options?
While options traders can make decent returns, beginners should not expect to get rich quick. Discipline and a successful trading strategy will be needed. Fortunately, one benefit of trading options is that traders cannot go negative – the premium is the maximum loss an investor can encounter.

