Stock Trading
Stock trading online is not just for institutional investors, millions of people buy and sell shares daily. This tutorial covers how to start stock trading, from reviews of the best apps to strategies for beginners. Use our ranking of the top stock brokers in the UK to start trading on the stock market today.
You can trade a dozen major indices, including the Dow Jones, NASDAQ and S&P 500 with competitive spreads at FXCC. However, it’s disappointing that FXCC doesn’t offer any individual stocks - a huge drawback against competitors like CMC Markets, which offers thousands of shares. RoboForex provides one of the broadest selections of real equities and stock CFDs spanning the US and 14 regional European markets, including direct access to the NASDAQ. It’s also one of the few brokers to offer a dedicated platform for stock trading, sporting leverage up to 1:20 and a robot builder that enables traders to automate and backtest stock trading strategies. There are hundreds of major global shares and indices available. You can also trade IPO shares and ETFs in the MT4 platform, depending on jurisdiction. You can expect a reasonable 0.1% commission on US shares, plus a range of analysis features to help you stay ahead of stock market news.Top 3 Stock Brokers UK
Complete List of UK Stock Brokers
Stock Trading Basics
Trading stocks online has become one of the most common ways for individuals and institutions to invest their capital, and stock markets are one of the cornerstones of the modern financial system.
Historians argue that stock trading existed in some form since ancient times. However, it started to take its current shape during the imperial age of the 17th century with the appearance of joint stock companies involved in intercontinental trade, such as the Dutch East India Company.
The London Stock Exchange and other exchanges began their life in this period in coffee houses and other gathering places where traders met to make deals on company shares and commodities.
Today, these exchanges have become some of the most respected and influential financial institutions in the world, and stock trading has become common among everyday working people all over the world. A recent survey revealed that a third of British people invested in stock markets, while that figure is even higher in the US where more than half of people buy and sell stocks.
Boom & Bust
Stock trading operates according to its own laws of gravity – as a general rule, what goes up must, at some point, come down. While it is true that stock markets almost always grow in the long run, they also tend to operate in a cycle of boom and bust periods, with growth interspersed by crashes and/or periods of stagnation.
Probably the most famous stock market crash of all time occurred in 1929, but there are plentiful examples from our own era. The dot com bubble crash in 2000, for example, knocked more than 50% off the value of the S&P 500, which tracks the top 500 US companies. The 2007 stock market crash knocked 57% off the index’s value, and the panic at the beginning of the Covid pandemic in 2020 resulted in a 35% nosedive – before the market rebounded to reach new record highs.
Periods when stock markets are buoyant are known as bull markets, while periods of poor performance are bear markets. Likewise, optimistic and pessimistic investors are known as bulls and bears, respectively.
Private Vs Publicly Traded Companies
There are a great many companies out there developing ground-breaking new products with the potential to make large profits, but it’s not possible to trade all of them.
A company has to be publicly traded for most traders and investors to be able to buy and sell shares in it. This usually involves an initial public offering, or IPO, in which shares in a company are offered to the public in a new stock issuance.
Quick Guide To Trading Stocks
The following stock trading 101 will lay out the basic steps to place your first trade. Next, more details about how to pick a suitable stock trading vehicle and brokerage are explained.
- Choose a broker – Use the criteria below to select the best stockbroker for your needs.
- Sign up – You will need to enter your personal information and usually verify your identity with official documents to open your account.
- Pick a stock – Do plenty of research and use our stock picking tips below to choose a stock that you feel confident trading.
- Place a trade – Follow the necessary steps on your trading platform to place a trade. Tip: use stop loss and take profit orders to keep a handle on your risk exposure.
- Monitor your trade – Keep an eye on the stock’s performance so you don’t miss the optimal time to exit your position.
- Close your position – If your trade has made a decent return or is close to your red line for losses, log into your stock trading platform and close your position.
Stock Trading Styles
Popular ways to trade stocks in the UK include:
- Day Trading – Day traders aim to make profits from price fluctuations that take place within a few seconds, minutes or hours and close all their positions by the end of the trading day. This allows them to avoid overnight fees and make a fresh start the next day, though the short timeframe may also limit their potential profit. As a result, day traders often use leverage to maximise their gains.
- Short-Term Trading – The definition of different timeframes in stock trading is subjective – short-term trades could be anything from a few hours to a few days. These short-term timeframes typically focus more on technical analysis and often make use of leverage.
- Medium-Term Trading – As the timeframe gets longer, fundamental analysis comes more into play and random market noise clears up. Medium-term traders will look at charts ranging back weeks or months and may plan trades around news events.
- Long-Term Trading – Some investors plan much longer trades that can be open for weeks, months or even years. These trades generally rely much more heavily on fundamental analysis.
- Buy-And-Hold Investing – Some individuals buy stocks and shares as a long-term investment rather than an asset to trade for profit. Buy-and-hold investors usually choose a selection of stocks and other assets that they view as having high growth potential and add to their position over time. Buy-and-hold investors may also benefit from dividend payments while growing their capital.
Stock Trading Vehicles
There are many ways to trade stocks, from buying and selling them directly to derivative vehicles:
- Direct Share Trading – The classic way of seeking profit from stock markets is to directly buy and sell shares in companies. Retail traders often do this through a middleman such as an online broker.
- Indices – Rather than investing in a single company, traders can speculate on a larger group of companies through an index. Indices are calculated by selecting a group of companies or assets that are representative of a market or sector as a whole. Some of the most famous indices include the FTSE 100 (UKX), which tracks the top companies in Britain, and the S&P 500 (SPX), which tracks the largest companies in the US. Traders can use indices as a basis for derivatives products or funds when stock trading.
- CFDs – A popular derivative product among retail traders that allows them to view and speculate on the price movements of shares and other assets without directly buying and selling them. CFDs can be traded with leverage and are widely available in the UK.
- ETFs – Exchange-traded funds allow traders to invest in or speculate on a selection of assets in one vehicle. Some ETFs track indices like the FTSE 100 or S&P 500, while others follow specific sectors by investing in relevant firms. Shares in ETFs can be bought and sold directly, or they can serve as underlying assets in derivatives.
- Spread Betting – A similar derivative to CFDs, with the added benefit that profits from spread betting are usually tax-free in the UK.
- Binary Options – A straightforward product in which the trader only has to choose a timeframe and predict whether a share or other asset’s price will rise or fall. The profit is pre-determined and remains the same regardless of the extent of price movements, making binary options good for short-term trading.
- Futures – This derivative contract is an agreement between counterparties to trade an asset for a specified strike price at an agreed future date. The profit or loss from this contract comes from the difference between the strike price and the market price when the contract expires. Futures contracts are standardised and typically sold on exchanges.
- Options – Similar to futures contracts, but with the added flexibility that the contract buyer purchases the right but not the obligation to execute the trade at the expiry date. This protects the buyer from excessive losses, which will be limited to the premium paid for the contract.
Other kinds of stock trading products include:
Fractional Shares
Stocks must typically be traded in full units – but with some companies’ stock worth thousands of pounds per share, this is not always accessible for individual investors.
The answer lies in fractional shares, an innovation offered by some brokers and dealers that allows individuals to buy fractions of shares by pooling their money with other buyers. This can be a good option for beginners looking to speculate on high-value stocks.
Penny Stocks
Generally, it is easy to find places to buy and sell shares of the biggest blue-chip companies, but some traders prefer to look for lesser-known companies that have more room to grow and tend to be more volatile.
Many of these stocks are valued at less than 1 British pound or less than 5 US dollars and are known as penny stocks. Trading penny stocks is highly speculative and can be rewarding, but it is also commensurately risky.
Trading Foreign Stocks
It is possible for UK investors to buy and sell stocks traded on numerous foreign stock exchanges, with US stocks and shares being the most widely available.
UK residents who want to trade foreign companies’ shares must ensure they are signed up with a brokerage that provides access to the right stock exchanges. They should also make sure they understand the rules for trading on that exchange, including any relevant tax laws for the country in question.
Most of the time, any tax due on these transactions will be automatically applied when you buy and sell the shares. However, there may be some ways to reduce the amount you are charged, so it is worth doing research.
For example, UK traders who access US shares are typically required to pay a 30% withholding tax on income from these investments such as dividends. However, by completing a W-8BEN form, they can reduce this amount to 15% when stock trading.
Shorting Stocks
If your analysis leaves you feeling pessimistic about the state of the market, you can always bet against a stock or index by going short.
Most of the time, bearish traders assume a short position through derivative products. However, there are alternatives such as the ProShares Ultra Short QQQ ETF (SQQQ). Investing in SQQQ and similar funds works in the same way as a leveraged bet against a security or index – in this case, against the Nasdaq-100 index.
Our experts share a detailed guide to shorting stocks further below.
Meme Stocks
One of the breakout stock trading stories of recent years is the rise of meme stocks – companies whose share price was catapulted to new heights thanks to online interest among meme-hungry retail traders.
Trading meme stocks involves staying in tune with online trading groups and placing bets on their favourite assets in the hope that they can repeat the success of the original meme stock, Gamestop (GME), in January 2021. The sudden spike of the stock can be seen in the TradingView snapshot below.
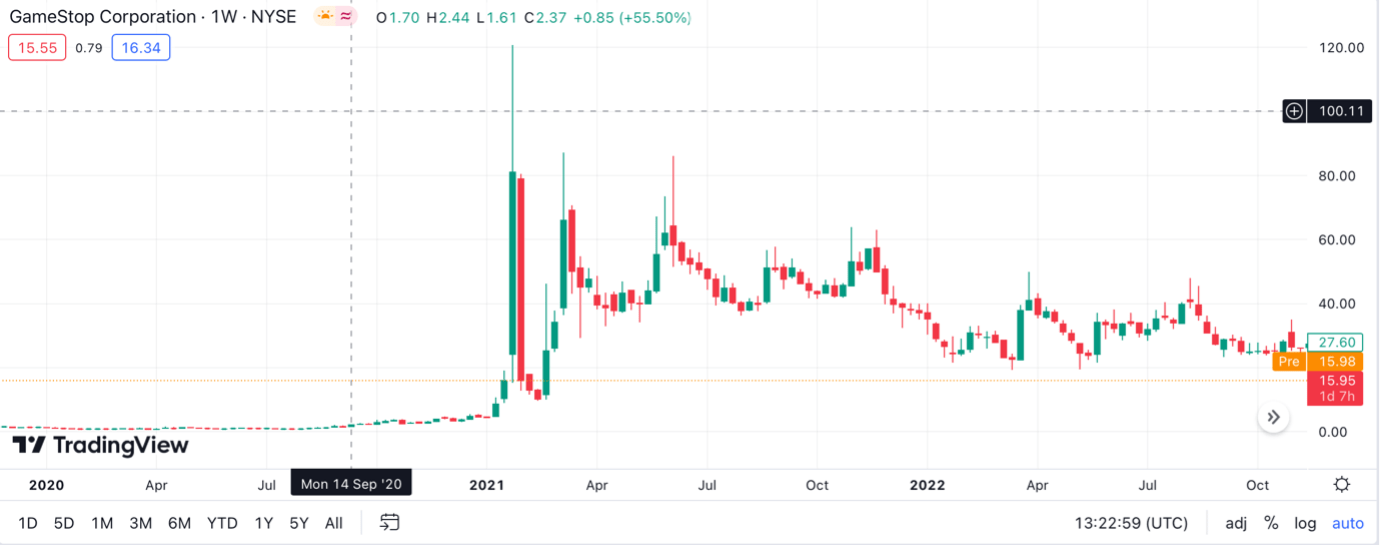
GameStop Price Chart
Stock Trading Strategies
There are countless strategies for trading stocks and shares, and investors should spend the time researching the ones that fit their financial goals, risk tolerance and trading style best.
With that said, key stock trading strategy considerations include fundamental analysis and technical analysis, and with good reason: these are two of the main tools traders use to analyse the markets.
- Fundamental analysis relies on reading real-world events and factors that influence the price of a stock or other asset. This can include general market news or events specific to a company such as new earnings reports. Fundamental analysis tends to be more useful over longer timeframes.
- Technical analysis refers to the analysis of price movements on charts. The aim of technical analysis is to identify patterns that help predict trends and potential reversals in the price movements of shares and other assets.
Fundamental Stock Analysis
 Fundamental analysis in stock trading concerns the intrinsic value of a stock in relation to its present and future valuation by the market. Questions a trader should ask are:
Fundamental analysis in stock trading concerns the intrinsic value of a stock in relation to its present and future valuation by the market. Questions a trader should ask are:
- What is the present market value of a stock in relation to a rational and objective valuation of the company’s performance and prospects?
- Is the present price of a stock representative of its actual value? In other words, is a stock presently undervalued, truly valued or overvalued on the basis of its present market price?
- Will a stock’s price correct itself to match its intrinsic value?
So the whole idea of using fundamental analysis is to determine the relationship of the present price of a stock and its intrinsic value, determine if the price matches that intrinsic value, and determine when the price will correct itself to match the intrinsic value depending on the circumstances and news items surrounding the stock in question.
The following data are used by traders when deciding on whether it is worthwhile to invest in a stock or not.
Earnings Reports
The earnings season is a period that the markets take seriously and is one that traders and investors look forward to. This is when the earnings reports are released. The earnings report not only tells investors how much money a company has made or lost, but also gives traders the following information:
- Earnings per share
- Price earning ratio (P/E ratio)
- Net income
- Net sales
The price-earnings ratio is especially important in measuring the valuation of a company. The lower the P/E ratio of a company, potentially the better the valuation of that company. A practical way of looking at a company’s valuation using the P/E ratio is to compare it with that of other companies listed in the same sector.
Earnings reports are released every three months, i.e. every quarter. They enable investors and shareholders to gauge the financial status of the companies in which they have investments in, and also in companies in which they may have an interest in investing in. The numbers seen in the earnings are not considered on their own, but are rather weighed against past numbers to see if there is an improvement in financial performance or a decline.
For instance, a company may release a report stipulating that they recorded a loss, but if the loss was much less than in previous quarters, investors will interpret this as a sign of changing fortunes and we will see demand for the stock. On the other hand, if profits declared miss estimates, demand will drop as investors offload the stocks of these companies. Google’s stock fell 10% on the day a disappointing Q3 report was released.
So investors can on the basis of the earnings reports, decide whether to pull out from a company, put money into a company or even increase the existing stake that they have in the company, and these factors will affect the share price of the company.
Introduction Of A New Product
Certain companies are known for their products. Talk of Apple and immediately people think about the iPhone, iPad and iPods. No one really associates Apple with their TVs or with any of their other products. The iPhone and iPad are the flagship products of Apple as a result of the revolution these products created in the world. They changed the way we make calls and use the internet. As such, anytime an upgraded iPhone or iPad comes up in the market, we see sales going through the roof and investors scrambling for the shares of Apple as a result of the perceived valuation of the company in the near future.
The Apple story is a clear example of how the introduction of a new product that creates a human revolution can change the financial outlook of that company, and in so doing, determines its value as perceived by investors.
Mergers & Acquisitions
Mergers and acquisitions have the same valuation effect on a company’s stock. If a struggling company is acquired by a much more powerful company, there will be an improved valuation on the shares of the acquired company. On the other hand, a merger between a strong company and an extraordinarily weak company can have a negative valuation on the shares of the former.
Government Policy
A government policy can radically change the perception of stocks in a particular sector, and increase the valuation and intrinsic values of the affected companies.
When the US Supreme Court upheld most of the provisions of the Affordable Care Act of 2012 (Obamacare), the stocks of Medicaid HMOs such as Molina, Amerigroup and Centene soared while those of health insurers dropped because of the income expectations that the law would have on both sets of companies. Health insurers would incur more costs by covering people with certain preexisting conditions, as well as compete with state-based insurance exchanges for clients, which could negatively impact their finances.
On the other hand, Medicaid HMOs would be able to make more money from the increased number of clients in the system. This is just one example of how a government policy could change the valuation of a company.
It will take some practice to fully understand how to use these parameters in fundamental analysis. The trader can practice this by looking at historical instances and applying them to present-day situations on a stock trading demo account in order to fully master the technique of trading stocks with fundamental analysis.
Technical Stock Analysis
Once you have selected a shortlist of stocks, you can also check their past performance using charts. How you set up your chart will depend on the length of trade you are envisaging – a day trader may be satisfied with a 1-day or 5-day view, for example. Conversely, a longer-term trader may turn to a longer timeframe – stock market outlooks for 1-month, 3 months and 6 months are common, as well as a year-to-date (YTD) graph view. Long-term stock market investors may go longer still by studying potential investments that go back as far as 5 or 10 years on a trading graph. Analysing price history provides a view of how the stock has performed during boom and bust periods and therefore can help forecast future trends.
Important information to look out for on stocks and shares trading graphs includes 52-week highs and lows, the trading volume during different time periods and the stock’s performance compared to the market in general and its competitors in the same sector. You may be able to find additional information, such as a 6 month outlook, by checking certain stock trading websites.
Stock traders should spend time learning about several technical analysis tools available as these are often important components in putting together a stock trading strategy:
- Moving Averages – These indicators aim to ‘smooth out’ the data on a chart by calculating and constantly updating averages, which will appear as a line on the chart. Traders frequently combine several moving averages from a range, with common MAs including 15-day, 30-day, 50-day and 200-day moving averages. These indicators are useful for determining trends; points where two moving averages cross can also forecast upcoming trend reversals.
- Bollinger Bands – This tool combines moving averages with volatility to help traders read charts and conduct technical analysis. The lower, upper and middle trendlines in the Bollinger Band are calculated using moving averages; the space between them indicates the current level of volatility, with a wider gap showing higher volatility.
- Stochastic Oscillator – This is used to determine whether a stock or other asset is currently overbought or oversold, using a scale from 0–100. A reading of 80 or more indicates that it is overbought, while 20 or lower indicates that it is oversold.
- Trading Volume – The trading volume is the amount of shares or units of another asset that are traded in a given timeframe. This is key information that is used as a component in many strategies, or can be used as an indicator in itself – for example, traders frequently check the trading volume during a trend reversal to understand whether the reversal is backed by a large number of trades and likely to take hold, or caused by only a small number of trades and likely to correct.
Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative analysis is the number-crunching method used to make trading decisions in the style often known as quant stock trading.
This involves analysing large swathes of data, usually using algorithms, automated trading models and machine learning. It is frequently used by pro traders in strategies such as high-frequency trading.
Guide To Short Selling
Short selling in the financial markets means borrowing an asset such as a stock from a broker to sell them at a high price, and then buying them back when prices have fallen so as to return the asset to the brokerage, and benefiting from the price differentials.
Short selling is used when there is an expectation that the price of an asset will fall within a space of time. Traders generally carry out short selling to make money from falling prices or they use it as a hedging strategy to protect themselves from a fall in prices on assets in which they have long positions.
Short Selling As A Hedging Strategy
For instance, a trader may be long on an imaginary stock we shall call XYS, and he may then decide to short sell the stock options on XYS. The strategy is played in such a way that if XYS has a bullish run if the trader is long on it, and the short sale option is out of the money as a result, then the cost of the short sale loss will be far less than the outcome of the long trade on the stock.
But if the price of XYS drops and puts the long position in a losing position, then the gains to be made from the short sale will far outstrip the loss on the long position on XYS. In this scenario, short selling XYS will act as a hedge trade.
Short Selling In A Falling Market
Traders can decide to employ short selling as a strategy to gain from falling prices, especially when the fall in prices is a systemic problem and not restricted to a sector or a single stock. This is why in the weeks following the collapse of Bear Stearns and preceding the collapse of Lehman Brothers in 2008 (the events that triggered the global financial crisis), traders massively engaged in short selling of stocks, especially those of the financial sector because they were all in a predictable free fall.
However, there is a very thin line to tread when trading a systemic fall in prices, because it gives room for the spreading of negative rumours and when everyone is selling, it tilts the equilibrium of the markets. Regulators will always step in when this occurs, and we have seen bans on naked short selling at various times when there is a systemic crisis. So if a trader wants to short sell as a profit strategy, then the best bet is to identify individual or sectorial assets based on technical and fundamental analysis, and short sell those assets with a bearish outlook.
Conditions For Profiting From Shorting
Short selling is an extremely risky strategy. If you are familiar with the collapse of MF Global, a financial services company that short sold the Euro in expectation of a fall in the value of the single currency in a massive bet that went horribly wrong, then you can imagine how risky the strategy is. A trader can lose a lot of money in an instant.
For a trader to be able to profit from short selling, the following parameters must be met:
- The trader must be able to locate an asset to use for short selling. To do this, the trader must have a trading account that provides enough margin for short selling, and also permits short selling.
- There must be enough liquidity in the asset to enable the short seller to get buyers of the asset at the market price.
- The price of the asset in question must experience a price drop to put the trade in a profit.
- The trader has to be able to buy them back at a lower price.
- The asset in question must not be one restricted from short selling by the regulatory authorities.
Shorting Advantages
Short selling is a very good way to trade a bearish expectation for an asset. There are many emerging market exchanges that only permit stock purchases, and traders can only make money from bullish runs. Trading in these markets can be frustrating because opportunities to make money are restricted. But with short selling, a trader’s opportunities to make money even from falling assets are limitless.
A good example of a profitable short sale was that performed by George Soros’s Quantum Hedge fund which made more than $1 billion in profit by short selling the British Pound in September 1992. Another trader who made money shorting a market is doctor-turned-investor Michael Burry, who made more than $600 million from short selling the credit default swap instruments on the US subprime housing market. Economists like Nouriel “Dr Doom” Roubini have regularly predicted periods of market crashes (he predicted the housing market bubble in 2005, long before prices began to tank), and such analyses easily form the basis for making huge profits from falling markets.
Short selling is also very useful for hedging and protecting profits. As was illustrated earlier in this article, short selling is a tool that allows traders to make up any losses incurred on the asset from unprofitable long positions. Many hedge funds that were long on stocks and stock markets used shorts to cover these positions and were able to use them to come out relatively unscathed when the cards came crashing in 2008.
How A Trader Can Make Money from Short Selling
A good target for a short sale would be an asset which is heavily overbought and whose fundamentals are not in tandem with its high prices. A good example of this was seen in an emerging market in Africa, where the brewery subsector was experiencing a massive price boom. There were questions over the state of health of some of the breweries whose stock prices were enjoying this sectorial boom, and a concerned investor decided to visit one of such breweries. He met overgrown weeds, a non-functional plant, a few workers and dilapidated structures. With this information, he quietly exited his holdings and within a short time, the information came out and the stock tanked. Such fundamental analysis is what is used to make informed decisions on what asset to short sell.
There are also technical indicators to consider. Is the asset forming a top or a bottom? There are several ways of identifying tops, bottoms, continuations and reversals on the charts. These can be used as a basis for a short sale. A short seller would be looking to sell a market top or a bearish reversal pattern.
Issues
The market bias of traders is partly influenced by market news, some of which are facts and some of which are rumours. Nothing causes market panic more than negative rumours. Part of what fuelled the systemic collapse of global stock markets in 2008 was fake market rumours following the collapse of Lehman Brothers. Many traders would enter short selling positions in certain assets, and then float negative rumours to force the asset price to tank so as to profit from these moves. From there on, it was a season of short selling which served to collapse the market further.
You can get an idea of how this works from the film Casino Royale, where the villain of the movie tried a terrorist attack on a new-design aircraft hoping to profit from the collapse of the airline’s shares (which never happened thanks to 007).
This and other unethical practices led to a ban on naked short selling by many regulatory bodies across the world. Today, several degrees of restrictions on short selling are still in place. So if you want to practice short selling, you need to be conversant with the rules in your jurisdiction so as not to run foul of the law.
Risk Management
A good stock trading strategy also has to be backed up by strong risk management to ensure the best chance of earning consistently and retaining profits.
Risk management can come in the form of precautions taken during trading, such as stop loss and take profit orders. These are orders that will automatically close a position if a certain level of loss or profit is reached. Stop losses can prevent large losses when the unexpected happens, while take profit orders ensure you lock in profit from a good trade.
Another way of controlling your risk exposure while trading stocks is through wallet management. This can involve setting a limit to the proportion of your total trading funds that you will risk in any one trade – 1% and 2% are common figures.
Choosing A Stock Broker
One of the most significant steps for anyone who starts trading stocks and shares is choosing a broker. This will have a direct impact on everything from your experience trading online to the fees you pay, so it is worth shopping around to find the best option.
Note that UK-based, FCA-regulated brokers have different rules to platforms overseen by foreign regulators, and some traders find the UK requirements to be restrictive. For example, the amount of leverage available from some foreign brokerages is far higher than their UK equivalents.
Another factor to consider is whether you want a straight stock trading account or a Stocks & Shares ISA. ISA accounts are a tax-efficient way to save money in the long term as they are exempt from capital gains tax. However, you likely won’t be able to trade derivatives on an ISA account and most offer less flexibility than non-ISA alternatives.
Other factors to consider include:
- Available assets & markets – Can you trade UK, US, European, Asian and Australian stocks?
- Trading vehicles – Can you buy stocks directly or speculate on price movements using derivatives like CFDs?
- Trading platform – Does the firm offer a reliable and stable platform and mobile app, such as MT4 or MT5?
- Fees – What are the share dealing charges, including any overnight fees for derivatives?
- Payment methods – Can you deposit and withdraw funds in GBP without fees and via popular payment methods?
- Tools & other resources – Does the brokerage offer useful extras like stock screeners, demo accounts and copy trading?
- Customer service – Is there a responsive support team on-hand during the hours you plan to trade stocks?
Stocks Available At AvaTrade
Stock Trading Platforms
Trading platforms are the terminals used to conduct research and execute trades, and as such are one of the most important tools for actively trading popular stocks such as Amazon and Apple.
If you’re wondering which stock trading app is best for beginners as well as more seasoned traders, thankfully many brands provide their clients with a proprietary platform that may be geared toward specific stock trading styles or client types. eToro, for example, is one of the easiest stock trading platforms to use and is ideal for casual traders and beginners.
It is also common to offer traders access to third-party stock trading programs. The most popular examples of these run powerful software that includes large amounts of tools to help with the analysis and execution of trades.
The most popular platforms for trading stocks include:
- MetaTrader 4 (MT4) – Although this was designed as a platform for forex trading, this powerful platform is frequently used for trading a far broader range of assets, making it one of the world’s most popular online trading terminals.
- MetaTrader 5 (MT5) – MT5 was developed as a successor to its popular forerunner, and since it was designed to be used for multi-asset trading, it is arguably even more useful for trading stocks and shares, with a wider range of analysis tools and order types, amongst other features.
Stock Trading Tools
Charts & Stock Trading Sites
Websites such as TradingView are useful for many traders as they give key information on a stock’s performance and allow you to set parameters and apply various tools. These include stock market summaries, real-time technical analysis overviews and live pricing charts with month-to-date (MTD) and year-to-date (YTD) performance stats.
Some other useful sites such as Yahoo! Finance also provide key information on individual companies.
Trading Robots
Automated trading can be helpful to many investors as they can execute stock trades automatically according to parameters set by the user. Though trading robots need to be frequently monitored to avoid unexpected losses, they are great for time-starved traders or for anyone who needs to execute a high volume of trades in a short space of time.
Trading robots operate algorithmically and are usually programmed using Python or another common language and can be found on specialised sites or on GitHub. Pre-programmed stock trading bots are also available on some popular platforms including MT4 and cTrader.
Mobile Apps
Being able to analyse stock quotes and conduct trades through the best stock trading apps is useful – it allows you to execute and monitor your trades while you go about your daily business and frees you from your laptop or desktop screen.
Fortunately, MT4 and other top trading platforms have mobile functionality.
Stock Screeners
One way to pick stocks is to use a stock screener. This tool allows you to select stocks by entering keywords and selecting tags. Traders can use the stock screener to whittle down the large number of stocks available through search terms, or create a shortlist by sorting the available stocks according to their chosen criteria.
Signals
Trading signals are alerts or trackers, usually sent by email or via a mobile app, that informs stock traders about significant market movements and news events.
A good signals app or add-on to your stock trading program can be a good way to keep up to date with your open trades and help you pick the best time to open and close positions.
Social Trading
Novices and people with little time to spend researching stock markets frequently turn to experienced traders for advice. Copy trading goes a step or two further, allowing them to fully benefit from experienced professional traders’ knowledge and experience by copying their trades.
Machine Learning
We are firmly in the age of AI, and stock trading is already taking advantage of machine learning tools, which help users analyse huge amounts of data to spot trends, run stock trading simulations and predict price action.
Stock Trading Tips & Tricks
- Start on a demo account. It’s a stock trading simulator that lets you practice and hone your skills through virtual trades, either via a web browser or mobile app. Demo accounts don’t require any deposits and are commission-free.
- You may need to spend hours planning and executing trades, so make sure your home stock trading office setup is equipped with one or more monitors large enough to display charts, a good keyboard, a responsive laptop, speedy internet and any other equipment to ensure you can trade in a comfortable setup.
- Though you will always have to pay some kind of fee to trade, there’s a large amount of competition among stock trading platforms. Look for zero-fee or other low-cost companies to ensure you retain your profits. Some of the best 0 commission stock trading apps include RoboForex and Avatrade.
- When you get started trading stocks, there will be a lot of terminology to learn and it can be challenging to understand the flood of new lingo and phrases. It’s worth noting down new vocabulary you learn to stay on top of this.
- The time of day you trade stocks is important, so get to know the market and the best time to trade. Keep in mind the 10 o’clock rule for stock trading, which states that the worst time to trade is around 10 a.m. We break down trading hours by major stock exchanges below.
- Keep a stock trading journal so you have a log and notes of the good and bad trades you have made and the reasons they succeeded or failed. This is also useful when the time comes to pay your taxes, as you can tally up your net profit or loss without trawling through old data. Many traders keep a journal using a template on Excel or Google Sheets, but there are also excellent journal apps and software available, including EdgeWonk and TraderSync.
- Study strategies that are relevant to the stock trading style and market you are aiming to trade. You can find a wealth of stock trading information and training in books, in videos and online.
- Join an online stock trading community and exchange your ideas and information on education forums or online chat sites. This is a good way to receive trading tips and newsletters, discuss your own ideas with knowledgeable people, and even find a mentor to help you sharpen your skills. It is also the best way to keep on top of stock trading memes that can sometimes forecast profitable new trends.
- If you feel that you have hit a plateau, try joining free professional online stock trading courses or attending lessons in person if there’s a suitable institute near you.
- There are many free stock trading videos and blogs available online, but you can also learn about trading on the move by listening to podcasts.
- Make sure you are using an efficient payment method to make deposits and withdrawals – currency conversion and transaction fees can quickly eat away profits, especially if you trade stocks with a brokerage based outside of the UK.
Pros Of Trading Stocks
- One of the most widely available asset classes at the best stock brokers and platforms
- Allows you to speculate on world-leading companies such as Shell, Tesla and Microsoft
- Trade exchanges and markets all over the world, including the UK, US and Europe
- Wide variety of derivatives and other trading vehicles to choose from, including CFDs
- Wide range of UK-regulated and trustworthy stock trading platforms and financial firms to trade with
Cons Of Trading Stocks
- Retail and institutional competition can make stock trading online difficult
- Stock markets often price in new information faster than individual investors can react
- Stock markets are not open 24 hours, unlike forex, cryptocurrency and some other asset classes
Rules & Regulations
Day trading and otherwise investing in stocks and shares in the UK is legal and thousands of non-professionals do it every day. However, there are some illegal stock trading practices such as insider trading or market manipulation that carry heavy penalties.
You are usually liable to pay tax on any profits you make from stock trading and other investments, depending on the account you hold and the type of investment.
When you buy a stock or share, it usually requires a period of T+2 days for the order to be settled. This means that you will need to wait two business days after the trade date. Traders can avoid waiting for this period by trading derivative products like CFDs, whereby you speculate on the rise or fall in share price without taking ownership of the underlying stock.
Different jurisdictions impose their own stock trading rules and restrictions on how traders are allowed to make cash purchases of stocks, such as freeriding and good faith violations in the US. Ensure you know the rules of any markets you trade.
Regulators have different rules and standards for the financial products on offer, and UK traders may be able to trade stocks with different trading vehicles or higher leverage through offshore firms.
UK Taxes
UK residents who make stock investments may have to pay tax when the investment is made and on profits they earn above an allowance.
The first relevant tax for stock trading online in the UK is stamp duty. For most individual investors, this is a 0.5% tax called the Stamp Duty Reserve Tax that may be automatically deducted when they buy shares through any electronic service. If the shares are bought through non-electronic means, the charge is only for transactions of over £1,000.
This tax is typically applied to UK shares, and will not be applied for shares in foreign companies – though you are likely to pay a separate charge or tax for these.
Profits from stock trading may also be subject to capital gains in the UK. This is a 10% (or 20% for those in a higher tax bracket) tax on profits made from stock investments that exceed a yearly allowance. In March 2023, the allowance stood at £12,300, but this was reduced to £6,000 in April, then will halve again to £3,000 the following year.
There is a ’30-day rule’ in the UK preventing stocks from being sold and re-bought shortly afterwards. This is designed to stop people from ‘resetting’ the capital gains of an asset by selling it at the end of the financial year before buying it again when the new year begins.
One way for UK residents to potentially avoid paying capital gains tax on their stock investments is by setting up an ISA.
Stock trading can also bring dividend benefits to traders who hold onto their assets, and these are also subject to tax. Dividends are currently taxed at 8.75% for taxpayers who are on an ordinary rate; 33.75% for those on a higher rate and 38.75% for those on the additional rate.
Taxes are applied to dividends earned above a yearly allowance, which stood at £2,000 but was halved to £1,000 in April 2023 with plans to halve it again the following year.
Trading Hours
- London Stock Exchange (XLON): 08:00am–4:30pm GMT
- New York Stock Exchange (XNYS): 09:30am–4:00pm GMT-5
- Nasdaq (XNAS): 9:30am–4:00pm GMT-5
- Euronext (ENX): 9:00am–5:30pm GMT+1
- Shanghai Stock Exchange (SHG): 9:30am–3:00pm GMT+8
- Japan Exchange Group (JPX): 9:15am–3:00pm GMT+5.30
- Australian Securities Exchange (XASX): 10:00am–4:00pm GMT+10
Premarket & After-Hours Trading
Many stocks are available to be traded during the hours before (premarket) and after (after-hours) the normal trading day closes.
These hours are usually set by the exchange, though the company and broker you trade with may set their own premarket and after-hours times for stock trading online.
Jobs In Stock Trading
Lots of people who invest in stock markets are individuals doing so with their own assets, but there are also many finance jobs related to stock trading for talented people with the drive to make it.
Though traders with a proven track record may also be considered by some companies, starting a stock trading job usually involves getting a degree or other relevant qualifications before anything else. A typical stock trading career will begin with classes or university courses followed by one or more internships or entry-level positions, before earning a position with more responsibility and a higher salary.
For a slightly different pathway to full-time stock trading jobs, keen amateurs may wish to try funded trading accounts, which provide capital to traders who prove their skills by completing certain challenges.
Alternatives To Stock Trading
- Forex is, alongside stocks, the most popular asset class to trade globally. A large variety of trading vehicles and firms are available for budding forex traders.
- Commodities such as gold, iron, corn and even livestock are traded around the world every day. Commodities are an excellent way to diversify your portfolio as many run counter to prevailing market trends.
- Cryptocurrency is the newest asset class. Cryptos have seen the most startling increases in the value of any assets over the last decades, but they are still largely unregulated, very volatile and extremely risky.
- Bonds are among the least risky instruments you can invest in, particularly if you opt for UK government-issued bonds known as gilts.
- Property remains a strong choice for long-term investment, with buy-to-let properties providing investors with a stable income combined with capital gains.
Bottom Line On Trading Stocks
Stock trading online is one of the most popular ways for people in the UK to grow their money, since it allows them to get a slice of the profits from public companies and to earn money by speculating on their performance. There are diverse options open to stock traders to suit almost every trading style as well as excellent software options for stock trading, and with such a variety of platforms on offer, you will find competitive prices and top-of-the-range features.
See our list of the best stock brokers to start trading.
FAQ
Is Stock Trading Halal Or Haram?
The simple answer is that Muslims are permitted to buy and sell stocks, and countries whose legal systems are based on Islamic law, such as Saudi Arabia and Iran, have their own stock exchanges.
However, not all trading vehicles comply with Sharia principles. Derivatives that involve paying interest, for example, may be considered haram, though brokers do increasingly offer Halal accounts.
The nature of the companies you trade shares in may also play a role. For instance, investing in publicly-traded companies that sell alcohol or tobacco may be considered haram.
If you are a Muslim and plan to start trading stocks and shares, you may want to consult a religious scholar before you start investing online.
How Does Stock Trading Work?
Simply put, the definition of stock trading is buying and selling stocks and shares of publicly-traded companies through an exchange. There are many different ways to do this, and for retail traders, the vast majority involve going through online brokers.
What Are The Different Types Of Stock Trading?
The different types of stock trading are often distinguished by the length of time trades remain open. For example, day trading involves opening and closing trades within one trading day. There are different styles of day trading, including high-volume scalping. Longer-term traders tend to use strategies such as position trading.
What Are The Differences Between Forex Trading And Stock Trading?
Stock trading involves buying and selling company shares, while forex traders speculate on the price movements of currency pairs. One of the major differences between the two is that stocks are generally traded during specific trading hours that generally coincide with a normal business day, while forex trading takes place 24/6 round the clock – only cryptocurrencies are traded 24/7.
How Can You Start A Stock Trading Business From Home?
All you really need to start earning money trading stocks is a good laptop or computer setup, an internet connection, careful research, a little starting capital and time. Since most trading can be done online and 24 hours a day, you can easily start stock trading on top platforms from your home.
Bear in mind that if you want to trade stocks as a business, you may need to log this with the tax office and your tax arrangements may change and you may be liable to pay income tax – make sure you research this thoroughly and seek professional advice before you register your business.
What Is The Best Stock Trading Platform?
What Is The Best Stock Trading App For Beginners?
There is no best stock trading app for beginners, but if you are new to trading you will probably want to use one that has an intuitive user interface and simple design. While you are learning the basics, you don’t need to pick an app that’s packed with advanced features – just choose one that’s easy to use and flexible enough for you to try out a few different approaches. Some of the top stock trading apps are designed to include powerful features but still be user-friendly, with the more advanced tools accessible through unobtrusive menus.
Beginners may also want to get a stock trading app that allows them to make virtual trades. Demo accounts are often packaged alongside live trading accounts, and they provide one of the best ways of learning to trade stocks through virtual markets where no real money is at risk.
Is Stock Trading Gambling?
No matter how carefully you plan your trades, there is often a degree of chance and luck involved in stock trading online, leading many to liken it to gambling. However, if you follow a consistent strategy and carefully stick to the criteria you set for picking stocks, you can eliminate much of the random chance from trading and take your fortunes into your own hands.
What Does It Mean When A Stock Stops Trading?
There are several reasons a stock might stop trading. One of these is that the company simply goes private after a buyout, meaning its shares will no longer be listed for sale on stock exchanges.
In some cases, trading on stocks and other assets may be temporarily halted for regulatory reasons, when a significant news announcement is upcoming, or when there are an excessive number of buy and sell orders on it.
What Is ‘Short’ In Stock Trading?
If you believe a company’s stock market value will increase in the future, you can buy a share today with a view to selling it later and pocketing the profit. This is called going ‘long’ in stock trading. If you think the share price will decrease, you can do the opposite – go ‘short’. This involves selling the share today and buying it back later at a lower price. This is achieved by essentially borrowing the shares that are sold and replacing them later.
What Are Options In Stock Trading?
Options are derivative products that give the contract buyer the right, but no obligation, to buy a stock or other asset at a specified price by the contract’s expiry date.
What Is Penny Stock Trading?
Penny stock trading involves the buying and selling of small company shares for less than $5 per share. Penny stocks are highly volatile due to their low market volume, so traders should be aware of the risks of trading such highly speculative products.
Is Stock Trading Worth It?
Millions of people around the world earn money by trading stocks. Whether trading is profitable for you depends on how much time you can invest in it, as like any skill it requires practice and patience to develop.
What Is A Limit Order In Stock Trading?
A limit order is an order to buy or sell a stock at a specific price. When you place a limit order, it will remain open until a market participant fills it, agreeing to buy or sell the stock at the specified price. The alternative is a market order, which will be automatically filled at the market price when it is placed.
Article Sources
The Advanced Stock Market And Day Trading Guide (Neil Sharp, 2019)
The UK Trader’s Bible (Dominic Connolly, 2010)
Financial Conduct Authority UK website (FCA)
UK Tax when you buy shares (GOV.UK)

